2025-08-15 hits:0 source:News
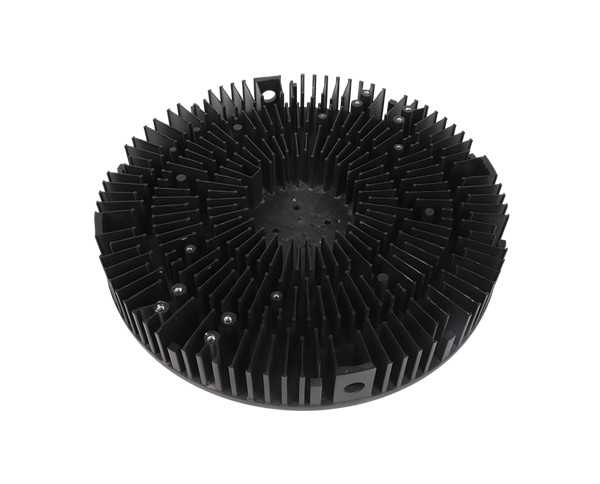

Complex cavity structures in die castings refer to intricate internal or external voids, recesses, or chambers designed to fulfill specific functional requirements, such as weight reduction, fluid flow, or component integration. These structures are increasingly common in advanced engineering applications, including automotive engine components, aerospace fuel systems, and electronic enclosures, where performance and space efficiency are critical.
Designing and manufacturing complex cavity structures pose unique challenges due to the need to maintain structural integrity, dimensional accuracy, and casting quality. One of the primary challenges is ensuring proper mold filling during the die casting process. Molten metal must flow into all areas of the cavity, including narrow channels and deep recesses, without trapping air or causing cold shuts. To address this, mold designers use computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations to optimize gating systems, ensuring uniform filling and minimizing turbulence. Multiple gates may be strategically positioned to facilitate complete filling of complex cavities, while overflow and venting systems remove trapped air and excess material.
Wall thickness distribution is another critical consideration. Complex cavity structures often have varying wall thicknesses, which can lead to uneven cooling and solidification, resulting in defects such as porosity, shrinkage cavities, or warpage. Designers aim for uniform wall thickness (typically 1.5-5 mm for aluminum alloys) to promote consistent cooling. Where thickness variations are unavoidable, fillets and radii are used to smooth transitions, reducing stress concentrations and improving metal flow.
Mold complexity is significantly increased when producing parts with complex cavities. The mold may require movable cores, slides, or lifters to form undercuts or internal cavities. These components must operate with high precision to ensure proper part ejection and dimensional accuracy. For example, a die casting with a complex internal cavity may require a collapsible core that retracts after solidification, allowing the part to be removed from the mold. The design of these core mechanisms must account for the high pressures and temperatures of the die casting process, ensuring durability and reliability.
Alloy selection is also important for complex cavity structures. Alloys with good fluidity, such as aluminum-silicon (Al-Si) alloys, are preferred as they can fill intricate cavities more easily. Additionally, alloys with high strength-to-weight ratios, such as magnesium alloys, are suitable for applications where weight reduction is a priority, even with complex cavity designs.
Quality control is more demanding for complex cavity structures, as internal defects may be difficult to detect. Non-destructive testing (NDT) methods, such as X-ray inspection and ultrasonic testing, are used to identify internal porosity or incomplete filling. Surface inspection techniques, including visual inspection and laser scanning, verify external dimensions and surface finish.
Advancements in die casting technology, such as high-pressure die casting (HPDC) and vacuum die casting, have improved the feasibility of producing complex cavity structures. HPDC uses high injection pressures (up to 150 MPa) to force molten metal into intricate mold cavities, while vacuum die casting removes air from the mold, reducing porosity and improving filling. These technologies, combined with advanced mold design and simulation tools, enable the production of complex cavity die castings that meet the stringent requirements of modern engineering applications.
Read recommendations:
extruded aluminum profiles suppliers
aluminium profiles for windows and doors
2020 aluminum extrusion near me
It is important to control the mold temperature during the zinc aluminum alloy die-casting process
lf you have any questions or comments, you can leave us a message and we will reply to you as soon as possible