2025-05-27 hits:0 source:News
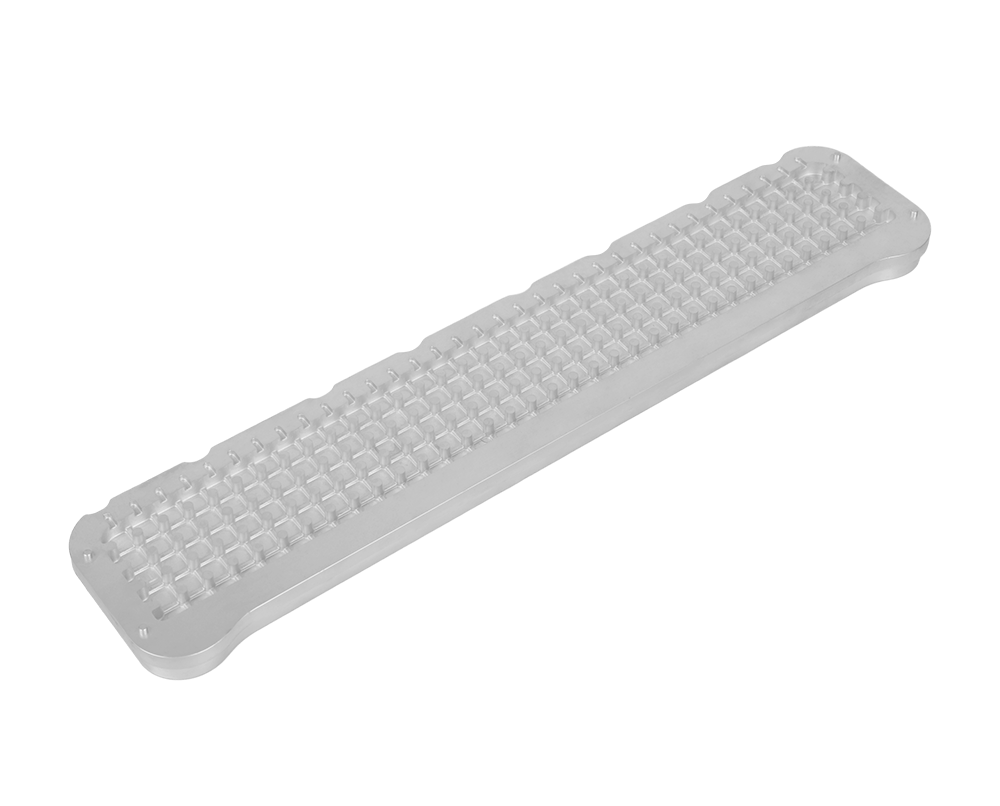

The manufacturing technology of pure aluminum die-casting heat sinks is a specialized field that combines the principles of die-casting with heat transfer engineering. Heat sinks are critical components in various electronic and thermal management systems, as they are designed to dissipate heat generated by high-power devices such as CPUs, GPUs, and power amplifiers. Pure aluminum is a preferred material for heat sinks due to its excellent thermal conductivity, lightweight, and cost-effectiveness.
The die-casting process for heat sinks starts with the design of the heat sink geometry. The design must optimize the surface area available for heat dissipation while ensuring structural integrity and manufacturability. Fin height, fin thickness, and fin pitch are key parameters that are carefully considered during the design phase. A higher fin height increases the surface area for heat transfer, but it also reduces the structural strength of the heat sink. Fin thickness and pitch need to be balanced to prevent issues such as bridging during the die-casting process and to ensure effective air or fluid flow for heat dissipation.
Once the design is finalized, the mold for the heat sink is fabricated. The mold is typically made of high-quality tool steel and is precision-machined to create the intricate fin structures. The mold's surface finish is also crucial, as a smooth surface reduces the resistance to the flow of molten aluminum and improves the quality of the heat sink's surface. In some cases, inserts or collapsible cores may be used to create complex internal geometries or to facilitate the removal of the heat sink from the mold.
During the die-casting process, molten pure aluminum is injected into the mold cavity at high pressure. Special attention is paid to the filling pattern to ensure that the aluminum fills the mold evenly and without creating voids or air pockets. After the aluminum solidifies, the heat sink is ejected from the mold. Post-casting operations may include trimming excess material, deburring, and machining to achieve the desired dimensions and surface finish.
To further enhance the heat dissipation performance of the die-cast heat sink, additional processes may be employed. For example, surface treatments such as micro-porous anodizing can increase the surface area and improve the wettability of the heat sink, which is beneficial for applications involving liquid cooling. In some cases, heat pipes or vapor chambers may be integrated into the heat sink to enhance the heat transfer efficiency, especially for high-power applications.
Read recommendations:
aluminium bifold door profiles
How can we improve the color change of aluminum alloy casting castings
lf you have any questions or comments, you can leave us a message and we will reply to you as soon as possible